Column Palletizing
| Column 1 | Column 2 |
|---|---|
| Row 1, Col 1 | Row 1, Col 2 |
| Row 2, Col 1 | Row 2, Col 2 |
| Row 3, Col 1 | Row 3, Col 2 |
| Row 4, Col 1 | Row 4, Col 2 |
| Row 5, Col 1 | Row 5, Col 2 |





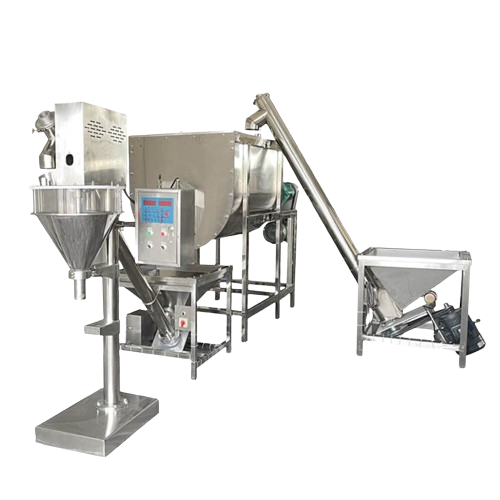
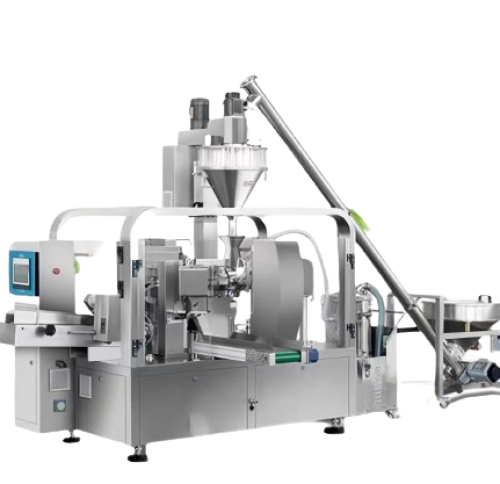
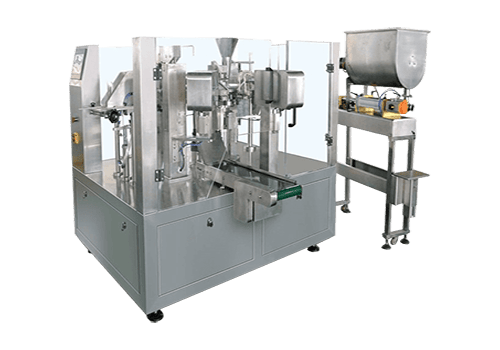
MeltVista Column Palletizing is a highly efficient automated handling and palletizing system, designed to accommodate a wide range of packaging types, including cartons and soft bags.
It can handle 400-550 bags or boxes per hour, automating the processes of handling and palletizing. This system replaces traditional methods where, in the past, workers had to manually move and stack items in production and storage environments. These manual processes were labor-intensive and inefficient, particularly in large-scale production settings, where meeting demand was often challenging.
In today’s society, palletizing machines have become essential equipment in the fields of smart manufacturing, automated production, and logistics. They are widely used across industries such as food, beverage, chemical, pharmaceutical, personal care, and construction materials.
Palletizing machines not only symbolize the modernization and automation of production and logistics but also represent core technologies for the development of future unmanned factories and warehouses.
Palletizing Machine Guide
Describe Overview Early Cargo Palletizing Modern Cargo Palletizing and Handling What are the Automatic Palletizers in Today's Society? Why Do We Need Column Palletizing?Structural Features
- This palletizing machine is built with a robust aluminum frame, providing stability and reliability. The machine’s claw-style gripper is equipped with pneumatic compression, opening, and closing functions to ensure precise handling and placement of materials. The servo system automatically adjusts the gripper spacing according to the size of the material, allowing it to accommodate various packaging specifications. The gripper is made of stainless steel, with gripper spacing consistent with the conveyor roller center distance, ensuring smooth and reliable gripping operations.
Working Principle
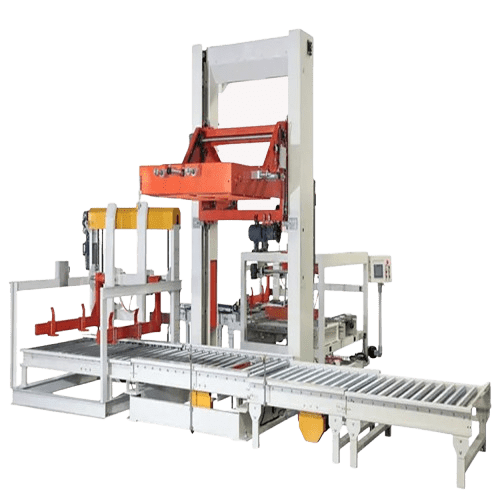
- Packaged materials are conveyed to the palletizing area, where the column robot operates with multiple axes to position the gripper directly above the material. Upon receiving the material positioning signal, the gripper moves down along the Z-axis to precisely grasp the material. The gripper then lifts and transports the material to the designated palletizing position. Once at the correct height, the material is safely placed on the pallet. This process repeats until the pallet is fully stacked. Upon completion, a buzzer alerts the operator to replace the pallet, allowing the machine to continue its operations in a seamless cycle.
Equipment Advantages
- The MeltVista column palletizing machine boasts a high load capacity of 160 kg and a flexible, high-speed palletizing rate of 400-550 bags/boxes per hour, meeting the demands of production lines of varying sizes. Its intelligent design ensures simple and fast operation, making it ideal for industries such as food, beverage, chemical, pharmaceutical, and more. Compared to traditional manual operations, this equipment significantly increases efficiency, reduces labor costs, and lowers the safety risks associated with repetitive tasks.
Application Scenarios
- With its wide applicability and advanced technical performance, the MeltVista palletizing machine has become a key piece of equipment in modern smart production and logistics management. It helps companies significantly boost production efficiency and automation.
- The MeltVista Column Palletizer is a highly efficient device designed specifically for automated handling and palletizing, developed to help businesses enhance production efficiency and reduce labor costs. Whether it's cartons or soft bags, the MeltVista Palletizer can quickly, safely, and accurately handle a variety of packaging materials. With a palletizing speed of 400-550 packages per hour, this equipment significantly boosts productivity on production lines and in warehouses, making operations simpler and more convenient.
1. Manual Palletizing
- Before automation, palletizing was almost entirely done manually. Workers would physically lift, carry, and stack goods layer by layer on pallets or designated areas. While flexible, this method was highly inefficient, particularly for handling large quantities or heavy goods, making it physically demanding.
- Advantages: Flexible, could handle various shapes, sizes, and weights of goods, no need for complex equipment.
- Disadvantages: Low efficiency, physically demanding, high risk of fatigue and injury, and the stacking process was prone to instability.
2. Hand Trucks or Dollies
- To ease the physical burden, simple mechanical aids like hand trucks or dollies were introduced. Workers used these tools to transport heavy loads to the palletizing area, reducing the need for long-distance manual lifting. However, the actual stacking was still done manually.
- Advantages: Reduced some of the physical strain, suitable for small to medium-sized loads.
- Disadvantages: Still labor-intensive and not much improvement in palletizing speed or efficiency.